Transaction
A transaction generally represents a unit of work within a database system. In the case of blockchain, a transaction is when an action signed by an account changes its state.
Transactions accepted by the network are stored permanently on blocks.
Transaction Types
There are different types of transactions. For example, you can transfer mosaics between accounts, transfer or configure the ownership of accounts (including the use of multisig rules), and more.
| Id | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mosaic | ||
| 0x414D | Mosaic Definition Transaction | Register a new mosaic. |
| 0x424D | Mosaic Supply Change Transaction | Change an existent mosaic supply. |
| Namespace | ||
| 0x414E | Register Namespace Transaction | Register a namespace to organize your assets. |
| 0x424E | Address Alias Transaction | Attach a namespace name to an account. |
| 0x434E | Mosaic Alias Transaction | Attach a namespace name to a mosaic. |
| Transfer | ||
| 0x4154 | Transfer Transaction | Send mosaics and messages between two accounts. |
| Multisignature | ||
| 0x4155 | Modify Multisig Account Transaction | Create or modify a multisig contract. |
| 0x4141 | Aggregate Complete Transaction | Send transactions in batches to different accounts. |
| 0x4241 | Aggregate Bonded Transaction | Propose many transactions between different accounts. |
| 0x4148 | Hash Lock Transaction | A deposit before announcing aggregate bonded transactions. |
| – | Cosignature Transaction | Cosign an aggregate bonded transaction. |
| Account restrictions | ||
| 0x4150 | Account Properties Address Transaction | Allow or block incoming transactions for a given set of addresses. |
| 0x4250 | Account Properties Mosaic Transaction | Allow or block incoming transactions containing a given set of mosaics. |
| 0x4350 | Account Properties Entity Type Transaction | Allow or block outgoing transactions by transaction type. |
| Cross-chain swaps | ||
| 0x4152 | Secret Lock Transaction | Start a token swap between different chains. |
| 0x4252 | Secret Proof Transaction | Conclude a token swap between different chains. |
| Remote validating | ||
| 0x414C | Account Link Transaction | Delegates the account to a proxy account to enable delegated validating. |
| Exchange | ||
| 0x415D | Add Exchange Offer Transaction | Create a new exhange offer. |
| 0x425D | Exchange Offer Transaction | Make exchanging. |
| 0x435D | Remove Exchange Offer Transaction | Remove a new exhange offer. |
| Drive | ||
| 0x415A | (Deprecated) Prepare Drive Transaction | Preparing a new drive. |
| 0x425A | (Deprecated) Join To Drive Transaction | Send a new join transaction to drive. |
| 0x435A | (Deprecated) Drive File System Transaction | Change a drive file system. |
| 0x445A | (Deprecated) Files Deposit Transaction | Block mocaics at the rate of a file size. |
| 0x455A | (Deprecated) End Drive Transaction | Terminate a drive execution. |
| 0x465A | (Deprecated) Drive Files Reward Transaction | Send rewarding for files. |
| 0x475A | (Deprecated) Start Drive Verification Transaction | Start verifying files storing. |
| 0x485A | (Deprecated) End Drive Verification Transaction | End verifying files storing. |
| Super Contract | ||
| - | Deploy Transaction | Deploying super contract. |
| - | Execute Transaction | Start contract executing. |
| - | Start Operation Transaction | Starting executing operation. |
| - | End Operation Transaction | Ending executing operation. |
| - | Operation Identify Transaction | Identifying execute operation. |
| Storage | ||
| 0x4662 | Replicator Onboarding Transaction | Replicator Onboarding |
| 0x4162 | Prepare BcDrive Transaction | Prepare a New Drive |
| 0x4262 | Data Modification Transaction | New Data Modification |
| 0x4462 | Data Modification Approval Transaction | Data Modification Approval. Inner transaction, sent by Replicators only |
| 0x4B62 | Data Modification SingleApproval Transaction | Inner transaction, sends Only by Replicators |
| 0x4562 | Data Modification Cancel Transaction | Cancel Data Modification |
| 0x4A62 | Storage Payment Transaction | Storage Payment |
| 0x4962 | Download Payment Transaction | Download Payment |
| 0x4362 | Download Transaction | New Download Channel |
| 0x4862 | Finish Download Transaction | Close Download Channel |
| 0x4C62 | Verification Payment Transaction | Verification Payment |
| 0x4F62 | End Drive Verification V2 Transaction | End Drive Verification. Inner transaction, sends Only by Replicators |
| 0x4D62 | Download Approval Transaction | Download Approval. Inner transaction, sends Only by Replicators |
| 0x4E62 | Drive Closure Transaction | Drive Closure |
| 0x4762 | Replicator Offboarding Transaction | Replicator Offboarding |
Defining a transaction
Transactions are defined in a serialized form. Each transaction extends from the transaction schema definition, combining the type's particular properties. You can find the description of the additional properties under the Schema section, at the end of each built-in feature description.
We recommend to use the xpx-chain-sdk to define transactions.
Fees
Transactions have an associated cost. This cost is necessary to provide an incentive for the validator who secures the network and runs the infrastructure.
The fee associated with a transaction primarily depends on the transaction’s size. The effective fee is the product of the size of the transaction, and a fee multiplier set by the Validator. The node owner can configure the latter value to all positive values, including zero.
effective_fee = transaction::bytes_size_to_be_validated * block::fee_multiplier
A sender of a transaction must specify max_fee during the transaction definition, meaning the maximum fee the account allows to spend for this transaction.
If the effective_fee is smaller or equal to the max fee, the validator can opt to include the transaction in the block.
The fee_multiplier is defined by validators, it is an integer value. It is stored in the block header, permitting to resolve which was the effective fee paid for every transaction included.
The validating nodes can decide their transaction inclusion strategy:
- Prefer-oldest: Preferred for networks with high transaction throughput requirements. Include first the oldest transactions.
- Minimise-fees: Philanthropic nodes. Include first transactions that other nodes do not want to include.
- Maximise-fees: Most common in public networks. Include first transactions with higher fees.
By default, the fee is paid in xpx, the underlying currency of the Sirius Chain network. Private chains can edit the configuration of the network to eliminate fees, or use another mosaic and namespace that better suits their needs.
Fee Tips
In short, validators need to define fee_multiplier, which is considered as fee per byte.
Max fee value is the lowest currency absolute value. eg. 5000 max fee = 0.005000 xpx.
The final transaction size might be increased from client/user site due to more complex transactions such as transactions with multisig accounts with extra cosigner information. Fee_multiplier will calculate with the final transaction size.
Signing a transaction
Accounts must sign transactions before announcing them to the network. Signing a transaction expresses the account’s agreement to change the network state as defined.
For example, a transfer transaction describes who is the recipient and the quantity of mosaics to be transferred. In this case, signing the transaction means to accept moving those mosaics from one account’s balance to another.
An account has to follow the next steps to sign a transaction:
- Get the
signing bytes, which are all the bytes of the transaction except the size, signature and signer. - Get the nemesis block generation hash. You can query
http://bctestnet1.brimstone.xpxsirius.io:3000/block/1and copymeta.generationHashvalue. - Prepend the nemesis block generation hash to the signing bytes.
- Sign the resulting string with the signer's private key. This will give you the transaction
signature. - Append the signer's signature and public key to the transaction to obtain the
payload. - Calculate the hash of the transaction applying the network hashing algorithm to the first 32 bytes of signature, the signer public key, nemesis block generation hash, and the remaining transaction payload.
Announcing a transaction
Signed transactions are ready to be announced to the network. You can either use the SDK TransactionHttp service or append the payload to the request of the transaction endpoint.
After announcing a transaction, the REST API will always return an OK response immediately. At this point, it is still unknown whether the transaction is valid.
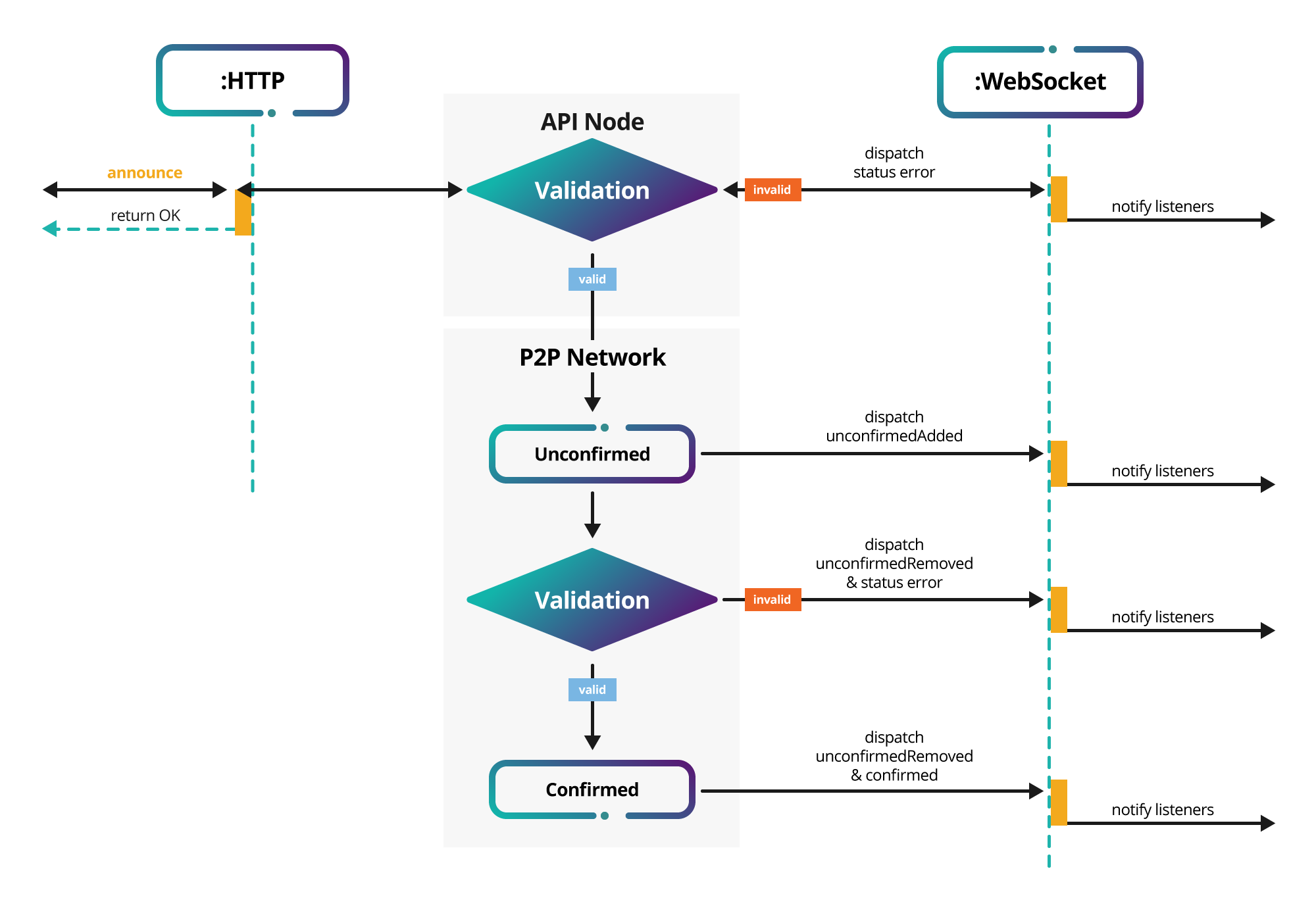
Transaction cycle
The first stage of validation happens in the API nodes. If the transaction presents some error, the WebSocket throws a notification through the status channel. In the positive case, the transaction reaches the P2P network with an unconfirmed status. Never rely on a transaction which has an unconfirmed state. It is not clear if it will get included in a block, as it should pass a second validation.
The second validation is done before the transaction is added in a validated block. If valid, the validator stores the transaction in a block, and it reaches the confirmed status.
Continuing the previous example, the transaction gets processed and the amount stated gets transferred from the signer's account to the recipient's account. Additionally, the transaction fee is deducted from the signer's account.
The transaction has zero confirmations at this point. When another block is added to the blockchain, the transaction has one confirmation. The next block added to the chain will give it two confirmations and so on.
Rollbacks
Blockchains are designed in a way that under certain circumstances, recent blocks need to be rolled back. These are essential to resolve forks of the blockchain.
The rewrite limit is the maximum number of blocks that can be rolled back. Hence, forks can only be resolved up to a certain depth too.
Sirius Chain has a rewrite limit of 360 blocks. Once a transaction has more than 360 confirmations, it cannot be reversed.
From experience, forks that are deeper than 20 blocks do not happen, unless there is a severe problem with the blockchain due to a bug in the code or an attack.
Guides
Monitoring a transaction status
Make sure a transaction gets included in the blockchain after being announced.
Schemas
Transaction
Inlines:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| max_fee | uint64 | The maximum fee allowed to spend for the transaction. |
| deadline | uint64 | The maximum amount of time to include the transaction in the blockchain. |
EmbeddedTransaction
Inlines:
SizePrefixedEntity
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| size | unit32 | The size of the transaction. |
