Writing your first application
This guide will take you through the Sirius Chain development cycle. You will send your first transaction to the blockchain after combining some Sirius Chain built-in features.
Background Information
The secondary ticket market, also known as the resale market, is the exchange of tickets that happens between individuals after they have purchased a ticket from an initial vendor. The initial vendor could be the event website, an online ticket vending platform, a shop or a stall at the entrance of the event.
Buying a ticket from someone that is not the initial vendor does not necessarily mean that the buyer needs to pay more for the ticket; there is a chance that the buyer can become a victim of buying a fake or duplicate ticket, where the initial original vendor cannot do anything to solve the issue.
What do we want to solve?
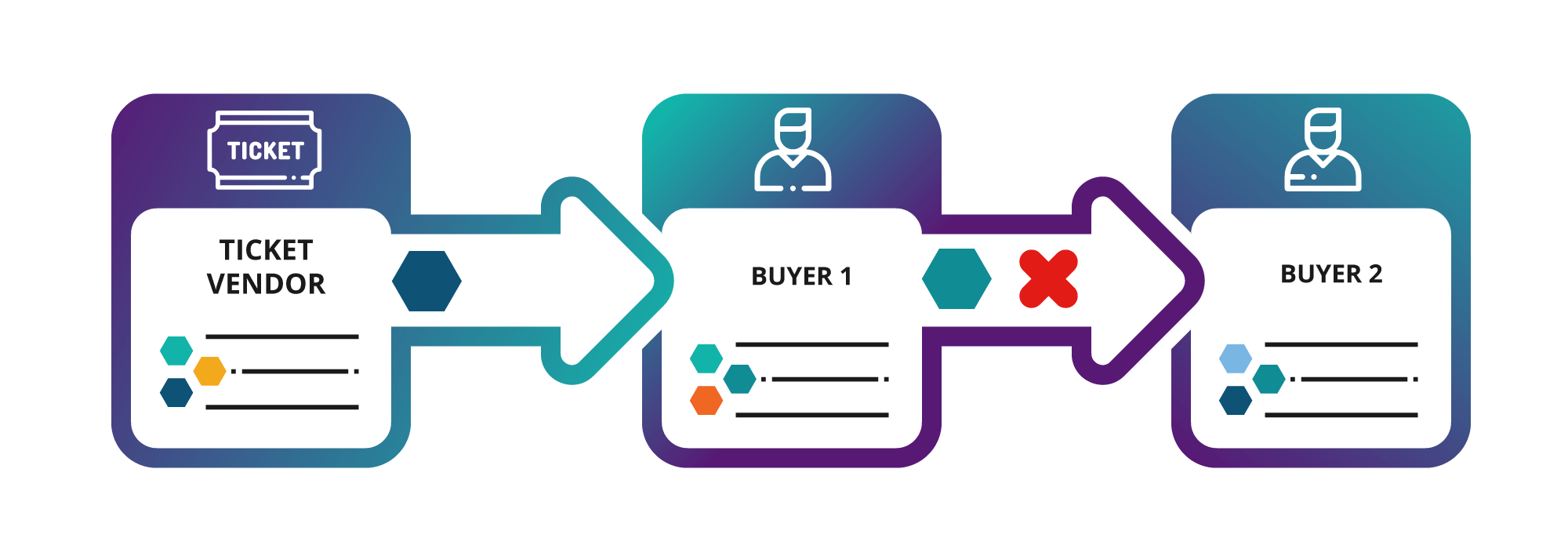
Authorisation model
The ticket vendor wants to set up a system to:
Identify each ticket buyer.
Avoid ticket reselling.
Avoid non-authentic tickets and duplicate ones.
Why should we use Sirius Chain?
Blockchain technology makes sense in cases where:
- There are different participants involved.
- These participants need to trust each other.
- There is the need to keep track of an immutable set of events.
Sirius Chain is a flexible blockchain technology. Instead of uploading all the application logic into the blockchain, you can use its tested features through API calls for transfer and storage of value, authorization, traceability, and identification.
The rest of the code remains off-chain. This reduces the inherent immutability risk, as you can change the process when necessary.
Prerequisites
- Finish getting started section
- Text editor or IDE
- XPX-Chain-SDK
- An account with
xpx
Getting into some code
Creating an account for each participant
First, we identify the actors involved in the problem we want to solve:
- The ticket vendor.
- The ticket buyer.
We have decided to represent the ticket vendor and buyer as separate accounts. Each account is unique and identified by an address. An account has access to a deposit box in the blockchain, which can be modified with an appropriate private key.
Have you loaded an account with test xpx? If it is not the case, go back to getting started section. The account you have created represents the ticket vendor.
- The following code will get the account info of
VAUOT2T4IRGFAY4WSD7DY3EUHANTRL3IAUG2TPNZ. Replace this address with your address created from the getting started section:
import { NetworkType, Address, AccountHttp, AccountInfo } from 'tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk';
const API_URL = 'https://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io';
const NETWORK_TYPE = NetworkType.TEST_NET;
const accountHttp = new AccountHttp(API_URL);
const getAccountInfoForAnAccount = () => {
//replace VAUOT2T4IRGFAY4WSD7DY3EUHANTRL3IAUG2TPNZ with your wallet address
const address = Address.createFromRawAddress('VAUOT2T4IRGFAY4WSD7DY3EUHANTRL3IAUG2TPNZ');
return accountHttp.getAccountInfo(address).subscribe(accountInfo => {
console.log('Account Address: '+ accountInfo.address.pretty());
console.log('Mosaics')
for (var index in accountInfo.mosaics){
console.log(accountInfo.mosaics[index].amount.toBigInt() + ":\t" + accountInfo.mosaics[index].id.toHex())
}
}, error => {
console.error(error);
}, () => {
console.log('done.');
});
}
getAccountInfoForAnAccount();
}
After running the above code, you should see on your screen an output similar to:
Account Address: VAUOT2T4IRGFAY4WSD7DY3EUHANTRL3IAUG2TPNZ
Mosaics:
50000000000: 13bfc518e40549d7
Note: In Testnet2, the mosaic ID of XPX is 13bfc518e40549d7 and XPX has a divisibility of 6 i.e 1000000 = 1 XPX
This account owns 50,000 XPX . If your own mosaics is empty, follow the previous guide instructions.
Create a second account to identify the ticket buyer.
import {Account, NetworkType, Address} from 'tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk';
const NETWORK_TYPE = NetworkType.TEST_NET;
const newAccount = Account.generateNewAccount(NETWORK_TYPE);
console.log('Ticker Buyer Account')
console.log('Private Key: ' + newAccount.privateKey);
console.log('Public Key: ' + newAccount.publicKey);
console.log('Address: ' + newAccount.address.plain());
Monitoring the blockchain
Accounts change the blockchain state through transactions. Once an account announces a transaction, if properly formed, the server will return an OK response.
However, receiving an OK response does not mean the transaction is valid, as it may not be included in a block. A good practice is to monitor transactions before being announced.
We suggest opening three new terminals:
- The first terminal monitors announce transactions validation errors.
import { Listener, Address } from "tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk";
const listener = new Listener('https://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io');
const subscribeStatus = (address: Address) => {
listener.open().then(() => {
const subscription = listener.status(address).subscribe(transactionStatusError => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(transactionStatusError));
}, error => {
console.error(error);
}, () => {
console.log('done.');
})
});
}
const address = Address.createFromRawAddress('VACQ54-STSYEZ-EA6IYE-H4WKOT-64W5DU-TOVFKI-LODB');
subscribeStatus(address)
- Monitoring
unconfirmedshows you which transactions have reached the network, but are not included in a block yet.
import { Listener, Address } from "tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk";
const listener = new Listener('https://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io');
const subscribeUnconfirmedAdded = (address: Address) => {
listener.open().then(() => {
const subscription = listener.unconfirmedAdded(address).subscribe(transaction => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(transaction));
}, error => {
console.error(error);
}, () => {
console.log('done.');
})
});
}
const address = Address.createFromRawAddress('VACQ54-STSYEZ-EA6IYE-H4WKOT-64W5DU-TOVFKI-LODB');
subscribeUnconfirmedAdded(address)
- Once a transaction is included, you will see it under the confirmed terminal.
import { Listener, Address } from "tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk";
const listener = new Listener('https://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io');
const subscribeConfirmed = (address: Address) => {
listener.open().then(() => {
const subscription = listener.confirmed(address).subscribe(transaction => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(transaction));
}, error => {
console.error(error);
}, () => {
console.log('done.');
})
});
}
const address = Address.createFromRawAddress('VACQ54-STSYEZ-EA6IYE-H4WKOT-64W5DU-TOVFKI-LODB');
subscribeConfirmed(address)
Creating the ticket
We are representing the ticket as a mosaic. Mosaics can be used to represent any asset in the blockchain, such as objects, tickets, coupons, stock share representation, and even cryptocurrency. They have configurable properties, which are defined at the moment of their creation. For example, we opt to set transferable property to false. This means that the ticket buyer can only send back the ticket to the creator of the mosaic, avoiding the ticket reselling.
- Create a mosaic named
ticket.
const vendor = PublicAccount.createFromPublicKey('<public_key>', NetworkType.TEST_NET)
const registerNamespaceTx = RegisterNamespaceTransaction.createRootNamespace(
Deadline.create(),
"company",
UInt64.fromUint(1000),
NetworkType.TEST_NET
);
const registerSubNamespaceTx = RegisterNamespaceTransaction.createSubNamespace(
Deadline.create(),
"ticket",
"company",
NetworkType.TEST_NET
)
const nonce = MosaicNonce.createRandom();
const mosaicId = MosaicId.createFromNonce(nonce, vendor);
const mosaicDefinitionTx = MosaicDefinitionTransaction.create(
Deadline.create(),
nonce,
mosaicId,
MosaicProperties.create({
"supplyMutable": true,
"transferable": false,
"divisibility": 0,
"duration": UInt64.fromUint(1000),
}),
NetworkType.TEST_NET
);
const mosaicSupplyChangeTransaction = MosaicSupplyChangeTransaction.create(
Deadline.create(),
mosaicId,
MosaicSupplyType.Increase,
UInt64.fromUint(1000000),
NetworkType.TEST_NET
)
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Divisibility | 0 | The mosaic won’t be divisible, no one should be able to send “0.5 tickets”. |
| Duration | 1000 | The mosaic will be registered for 1000 blocks. |
| Initial supply | 1000000 | The number of tickets you are going to create. |
| Supply mutable | true | The mosaic supply can change at a later point. |
| Transferability | false | The mosaic can be only transferred back to the mosaic creator. |
Although the transaction is created, it has not been signed and announced to the network yet.
- Sign the transaction with the ticket vendor account first, so that the network can verify the authenticity of the transaction.
Note
To make the transaction only valid for your network, include the first block generation hash. Open http://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io:3000/block/1 in a new tab and copy the meta.generationHash value.
const privateKey = "<private_key>";
const account = Account.createFromPrivateKey(privateKey, NetworkType.TEST_NET);
const signedTransaction = account.preV2Sign(transferTransaction, generationHash);
- Once signed, announce the transaction to the network.
const transactionHttp = new TransactionHttp('http://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io:3000');
transactionHttp.announce(signedTransaction).subscribe(
x => console.log(x),
err => console.log(err)
);
- Copy the mosaicId returned in the
monitor confirmedtab after the transaction gets confirmed.
... MosaicId:7cdf3b117a3c40cc ...
Sending the ticket
Send one company:ticket to the ticket vendor account announcing a transfer transaction, one of the most commonly used actions in Sirius Chain.
- Prepare the transfer transaction. Three main attributes form a transfer transaction:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Deadline | 1 Hour | The maximum amount of time to include the transaction in the blockchain. |
| Recipient | VC7A4H…2VBU | The recipient account address. |
| Mosaics | [1 7cdf3b117a3c40cc] | The array of mosaics to send. |
| Message | enjoy your ticket | The attached message. |
| Network | TEST_NET | The local network identifier. |
address, err := sdk.NewAddressFromRaw(os.Getenv("ADDRESS"))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
mosaicId, err := sdk.NewMosaicId(srtconv.ParseUnit(os.Getenv("MOSAIC_ID"), 16, 64))
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
transferTransaction, err := client.NewTransferTransaction(
sdk.NewDeadline(time.Hour),
address,
[]*sdk.Mosaic{sdk.NewMosaic(mosaicId, 1)},
sdk.NewPlainMessage("enjoy your ticket")
)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
import {
Account, Address, Deadline, UInt64, NetworkType, PlainMessage, TransferTransaction, Mosaic, MosaicId,
TransactionHttp
} from 'tsjs-xpx-chain-sdk';
var mosaicId = new MosaicId("7CDF3B117A3C40CC");
const transferTransaction = TransferTransaction.create(
Deadline.create(),
Address.createFromRawAddress('VC7A4H-7CYCSH-4CP4XI-ZS4G2G-CDZ7JP-PR5FRG-2VBU'),
[new Mosaic(mosaicId, UInt64.fromUint(1))],
PlainMessage.create('enjoy your ticket'),
NetworkType.TEST_NET
);
import io.proximax.sdk.model.account.Address;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.blockchain.NetworkType;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.mosaic.Mosaic;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.mosaic.MosaicId;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.transaction.Deadline;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.transaction.PlainMessage;
import io.proximax.sdk.model.transaction.TransferTransaction;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit.HOURS;
BigInteger mosaicId = new MosaicId("7CDF3B117A3C40CC").getId();
final TransferTransaction transferTransaction = TransferTransaction.create(
Deadline.create(2, HOURS),
Address.createFromRawAddress("VC7A4H-7CYCSH-4CP4XI-ZS4G2G-CDZ7JP-PR5FRG-2VBU"),
Arrays.asList(new Mosaic(mosaicId, BigInteger.valueOf(1))),
PlainMessage.create("enjoy your ticket"),
NetworkType.TEST_NET
);
Although the transaction is created, it has not been announced to the network yet.
- Sign the transaction with the ticket vendor account first, so that the network can verify the authenticity of the transaction.
Note
To make the transaction only valid for your network, include the first block generation hash. Open http://api-2.testnet2.xpxsirius.io:3000/block/1 in a new tab and copy the meta.generationHash value.
account, err := sdk.NewAccountFromPrivateKey(os.Getenv("PRIVATE_KEY"), networkType, generationHash)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
signedTransaction, err := account.sign(transferTransaction)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
const privateKey = "<private_key>";
const account = Account.createFromPrivateKey(privateKey, NetworkType.TEST_NET);
const signedTransaction = account.preV2Sign(transferTransaction, generationHash);
final String privateKey = "<private_key>";
final Account account = Account.createFromPrivateKey(privateKey, NetworkType.TEST_NET);
final SignedTransaction signedTransaction = account.sign(transferTransaction, generationHash);
- Once signed, announce the transaction to the network.
_, err = client.Transaction.Announce(context.Background(), signedTransaction)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
const transactionHttp = new TransactionHttp('http://bctestnet1.brimstone.xpxsirius.io:3000');
transactionHttp.announce(signedTransaction).subscribe(
x => console.log(x),
err => console.log(err)
);
final TransactionHttp transactionHttp = new TransactionHttp("http://bctestnet1.brimstone.xpxsirius.io:3000");
transactionHttp.announceTransaction(signedTransaction).toFuture().get();
- When the transaction is confirmed, check that the ticket buyer has received the ticket.
$> xpx2-cli account info --profile buyer
What’s next?
Did you solve the proposed use case?
- Identify each ticket buyer: Creating Sirius Chain accounts for each buyer.
- Avoid ticket reselling: Creating a non-transferable mosaic.
- Avoid non-authentic tickets and duplicate ones: Creating a unique mosaic named
company.ticket.
Continue learning about more Sirius Chain built-in features.
