Node
The Sirius Chain platform is built from a network of nodes. These nodes provide a powerful, stable, and secure platform where Smart Assets transactions are conducted, searched, and immutably logged to the blockchain ledger.

What is the Sirius Chain’s Performance Advantage?
The four-layered architecture allows developers to update any of these tiers without disrupting the others, which improves security.
P2P Component
Repository: Sirius Chain Server

Peer node communication
The P2P nodes form the backbone of the blockchain, making the network robust since it cannot be shut down by eliminating a single entity. The role of the node is to verify transactions and blocks, run the consensus algorithm, create new blocks, and propagate the changes through the network.
The API nodes push new transactions to the P2P network, where they are included in a block or discarded. After the block is processed, the node saves:
- The binary of each block as a flat-file on disk.
- The updated chain state in memory or RocksDB (configurable).
RocksDB
RocksDB stores the chain state. The data structures cached are serialized and stored as value to a corresponding key. For example, a column maps the public keys to addresses. Another one, the account state entries as the value to corresponding address keys.
Storing the state in memory is usually faster than using RocksDB. However, storing state information in RocksDB demands less memory of the network nodes.
Note
Persisting the state in RocksDB is convenient in networks with a large number of accounts.
API Component
Repository: Sirius Chain Server
API node communication
P2P nodes can be configured to have an API layer. The primary responsibility of the API is to store the data in a readable form in MongoDB.
The API verifies transactions received from the REST component. Additionally, the broker process that stores changes in MongoDB, forwards them to ZMQ.
This component is also responsible for collecting the cosignatures of aggregated bonded transactions, which are only processed once they are complete.
MongoDB
MongoDB stores blocks, transactions, and chain states for high query performance.
The broker service updates the linked MongoDB instance when:
- A new block / a bunch of blocks finish processing.
- New unconfirmed transactions complete processing.
Note
MongoDB should not be accessed externally.
ZMQ
ZeroMQ is an asynchronous messaging library, which enables real-time subscriptions. It transports notifications from the API node to the ZMQ endpoint, where Sirius Chain REST listens. It is an alternative to REST WebSockets, aimed to be used when performance is critical.
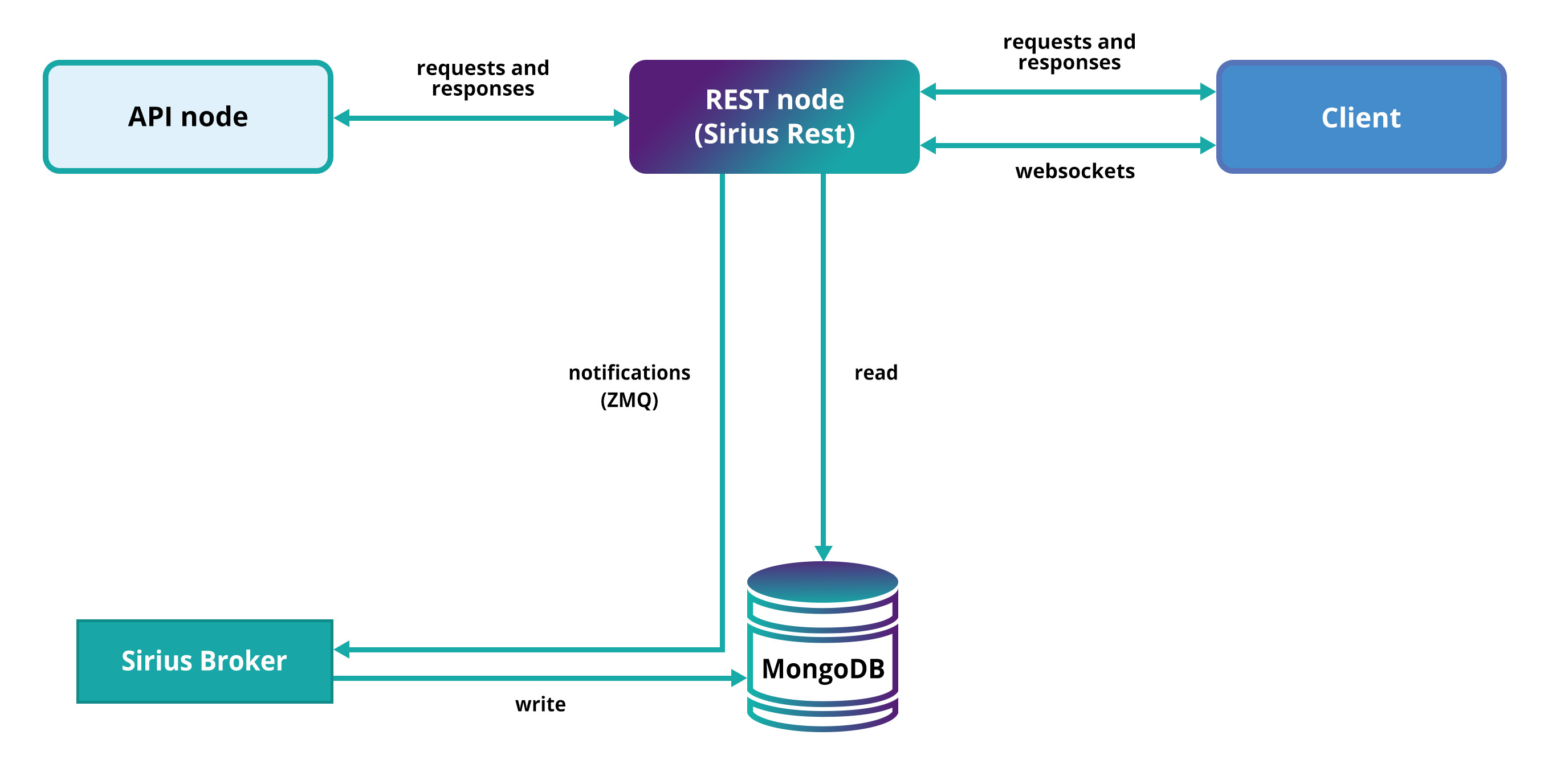
REST node
Repository: Sirius Chain REST (Repo is not yet ready open to public)

REST node communication
The REST nodes handle JSON API client requests. A node reads from MongoDB, formats the response, and returns it to the client. This component is also responsible for returning events to the client using WebSockets.
Each REST node connects to one API instance to send new transactions requests triggered from the client-side and receive updates in real-time using sockets.
Guides
- Running Sirius Chain locally (upcoming)
Deploy a Sirius Chain full node for learning and development purposes.
- Deploying a testnet node (upcoming)
- Configuring a private network (upcoming)
- Creating a custom plugin (upcoming)
